Digital Fluorescein Angiography
Fluorescein Angiography is a method that allows the depiction of the posterior part of the eye and more specifically the vessels of the retina, the optic nerve, the macula and the peripheral retina.
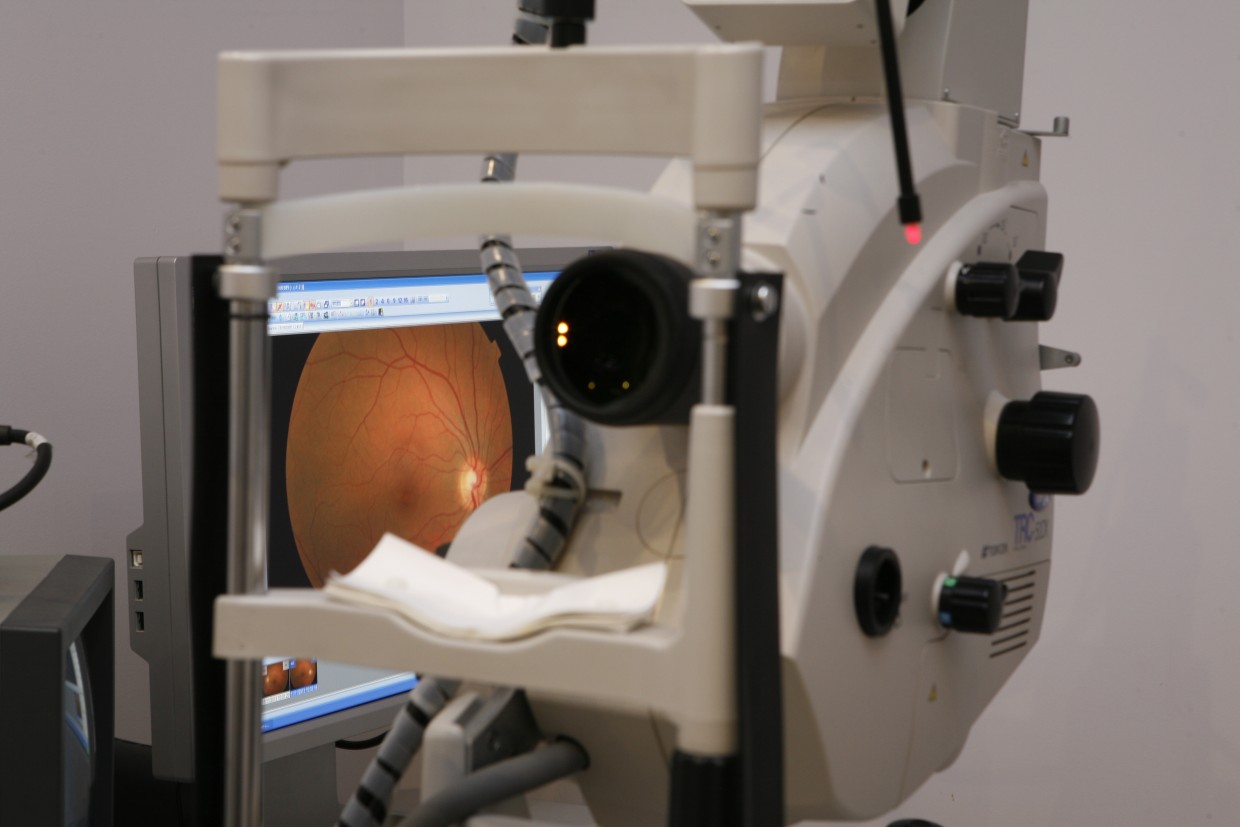
Digital Fluorescein Angiography
Fluorescein angiography is necessary for the diagnosis and monitoring of various diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and macular disease, retinal vein or artery occlusions, inflammations, macular dystrophies, degenerative diseases of the fundus, optic neuritis and autoimmune diseases. It also serves as a guide for the treatment of certain retinal conditions.
Fluorescein angiography is performed through the instillation of mydriatic eye drops to dilate the pupil and then perform an intravenous injection of an orange dye called fluorescein. While fluorescein circulates in the eye vessels, images of the posterior part of the eye are captured using a special camera (digital fundus camera). The examination lasts approximately 5-10 minutes.
For approximately 24 hours after the examination the patient may notice a yellowing of the skin and urine. During the examination, some patients may experience nausea, allergic reaction to the dye and, in rare occasions, fainting.
For that reason, the examination is always performed in the presence of an anesthesiologist, to handle any complications.
Contraindications to fluorescein angiography include: allergies to medications or contrast dyes, renal impairment, pregnancy.
